Diagnostic Equipment
This category includes devices used to identify and evaluate medical conditions.
Common Products:
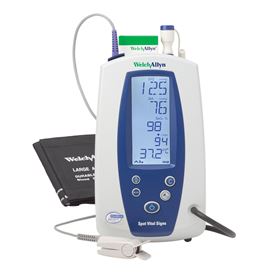
• Vital Signs Monitors: Measure blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature.
• ECG/EKG Machines: Record the electrical activity of the heart for detecting cardiac issues.
• Ultrasound Devices: Imaging equipment for viewing internal organs.
• X-Ray Machines: For imaging bones and internal structures.
• Blood Analyzers: Devices for analyzing blood components.
Applications: Diagnosis of diseases, monitoring patient conditions, and detecting vital signs.
Surgical Equipment
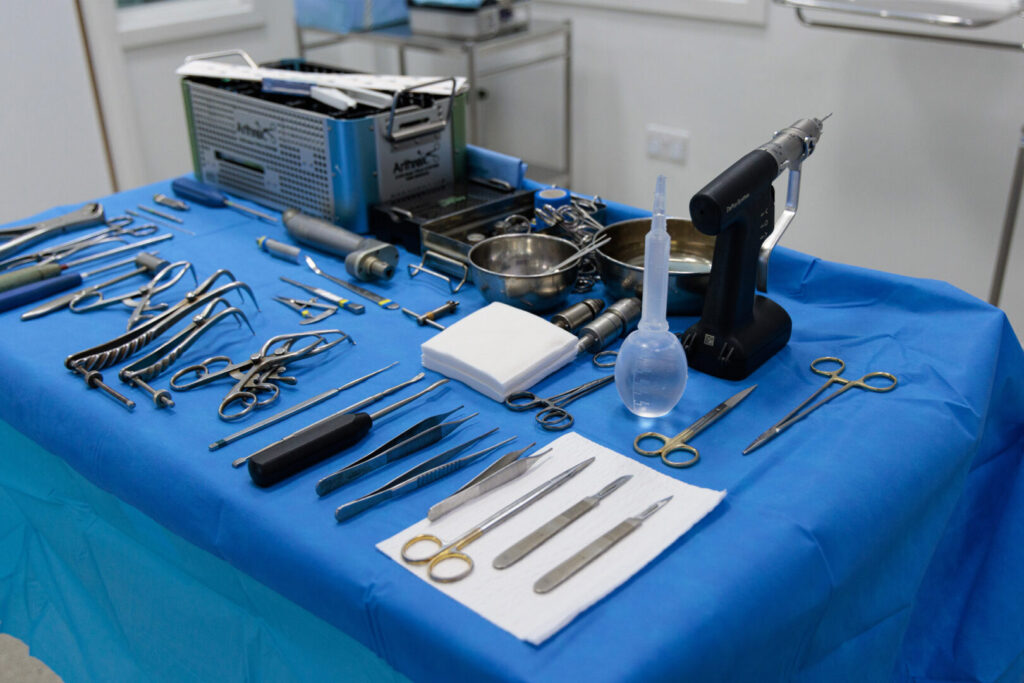
This category includes instruments and devices used in surgical procedures.
Common Products:
• Surgical Lights: Provide precise illumination during surgeries.
• Surgical Microscopes: Magnify surgical areas for precision procedures.
• General Surgical Instruments: Scalpels, forceps, surgical scissors, and electrocautery devices.
• Laparoscopic Devices: Instruments for minimally invasive surgeries.
Applications: General surgeries, specialized operations, and microsurgeries.
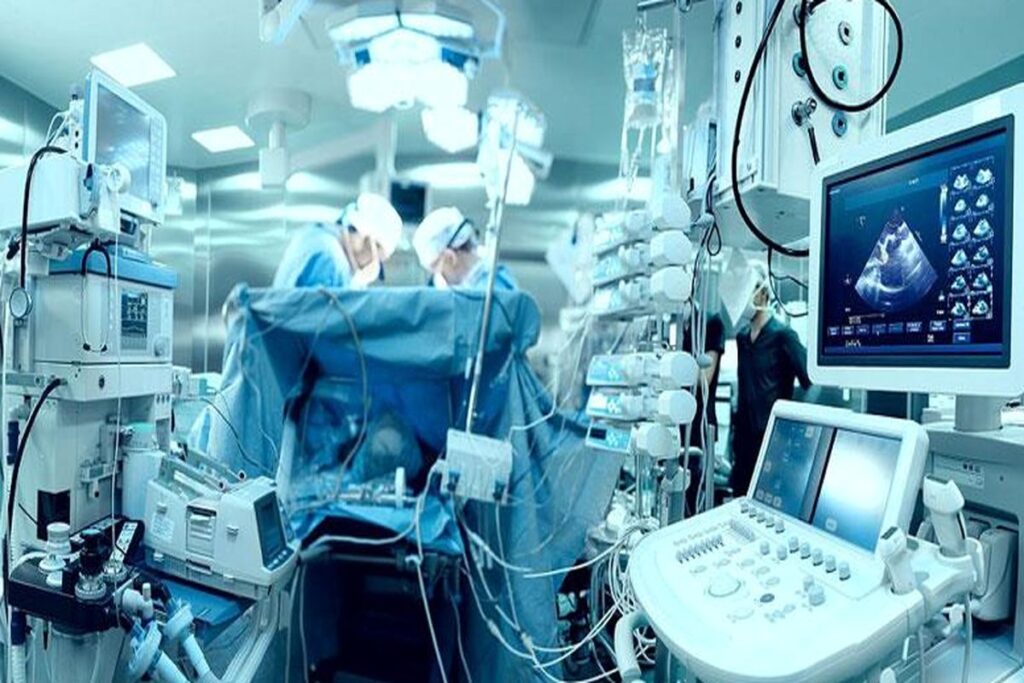
Hospital Equipment
These are essential devices for patient care in hospitals.
Common Products:
• Hospital Beds: Adjustable beds with advanced features such as electric controls.
• Oxygen Concentrators: Provide a steady supply of oxygen for patients.
• Infusion Pumps: Deliver precise doses of fluids or medications.
• Central Monitoring Systems: Monitor ICU patients’ vital signs.
Applications: Patient care in ICUs, emergency rooms, and general wards.
Home Care Equipment
Designed for patients who need care and treatment at home.
Common Products:
• Digital Blood Pressure Monitors: For accurate blood pressure measurement.
• Portable Oxygen Concentrators: Lightweight devices for patients with respiratory issues.
• Nebulizers: Deliver medication as a mist for asthma or respiratory diseases.
• Air Mattresses: Prevent bedsores for bedridden patients.
Applications: Improving patient comfort and reducing the need for hospital stays.
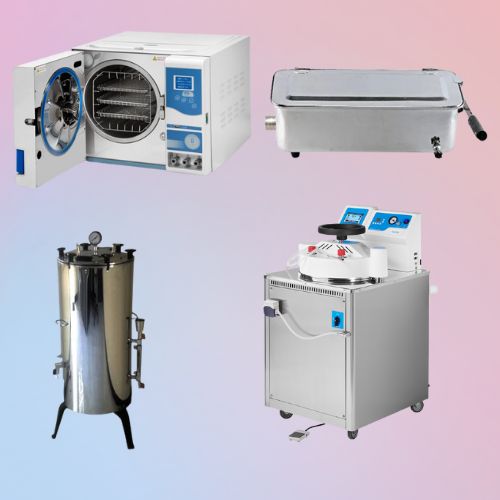
Sterilization Equipment
This category includes tools for sterilizing medical instruments and environments.
Common Products:
• Autoclaves: Sterilize surgical instruments with steam.
• UV-C Devices: Disinfect surfaces and environments with ultraviolet light.
• Washer-Disinfectors: Wash and disinfect medical tools.
Applications: Ensuring hygiene and preventing infections.

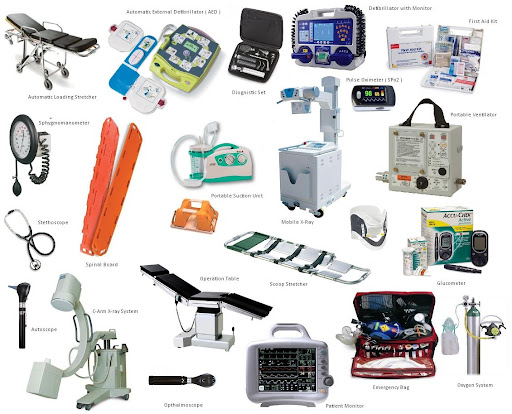
Emergency Equipment
These devices are used in urgent medical situations to save lives.
Common Products:
• Defibrillators: Restore normal heart rhythm during cardiac arrest.
• First Aid Kits: Contain essential tools for immediate care.
• Stretchers: Safely transport patients.
• Ventilators: Assist patients with breathing in critical conditions.
Applications: Quick response in emergency and critical care scenarios.

Diagnostic Equipment
Vital Signs Monitors
• Purpose: These devices measure key indicators of a patient’s health, such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation.
• Use Cases: Commonly used in hospitals, clinics, and emergency care to monitor patients’ conditions continuously.
• Examples: Portable monitors for bedside care, handheld devices for quick checks.

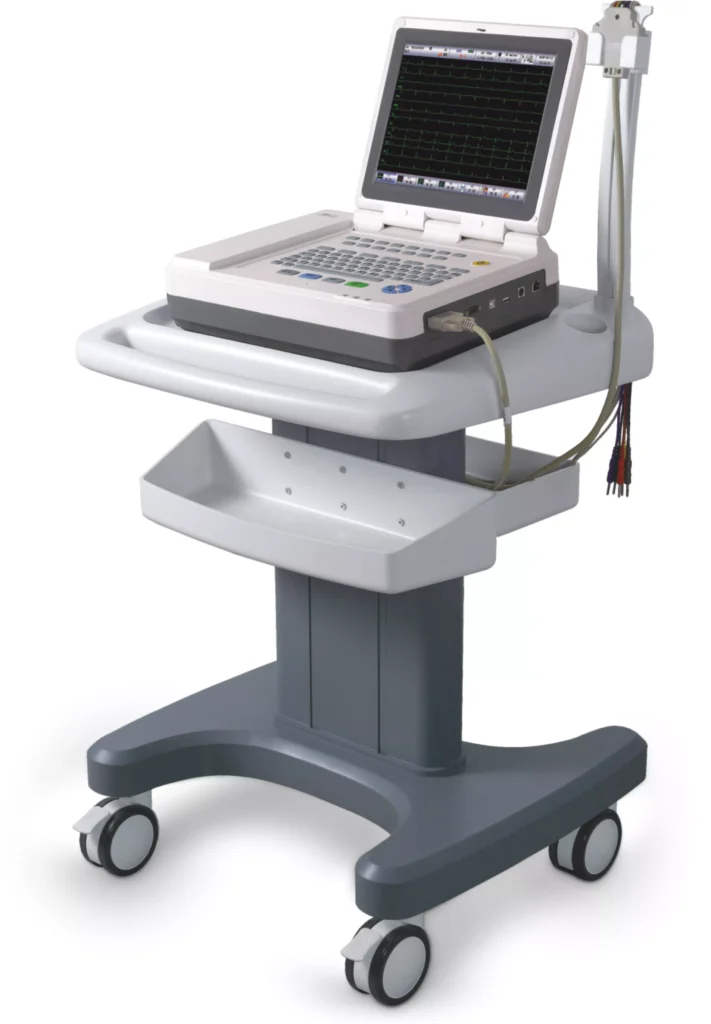
ECG/EKG Machines (Electrocardiogram)
Purpose: Record the electrical activity of the heart to detect arrhythmias, heart attacks, or other cardiac issues.
• Use Cases: Used in cardiology clinics, hospitals, and emergency departments to evaluate heart health.
• Features: 12-lead ECG machines for detailed analysis, portable ECG devices for ambulatory monitoring.
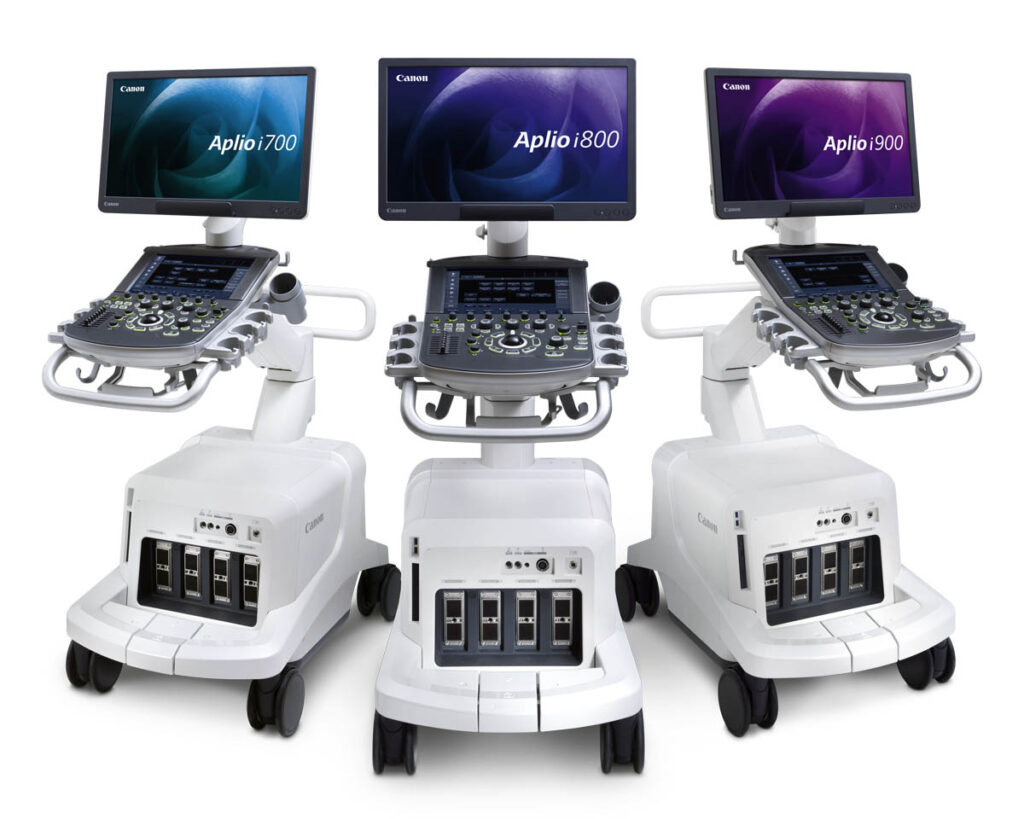
Ultrasound Machines
Purpose: Use sound waves to create images of internal organs, tissues, and blood flow.
• Use Cases: Widely used in obstetrics (pregnancy monitoring), cardiology, urology, and general diagnostics.
• Types: Handheld portable ultrasounds and advanced 3D/4D imaging systems.
X-Ray Machines
Purpose: Produce images of bones, lungs, and other internal structures using X-rays.
• Use Cases: Essential for detecting fractures, infections (e.g., pneumonia), and other abnormalities.
• Advancements: Digital radiography systems that provide clearer images and reduce radiation exposure.
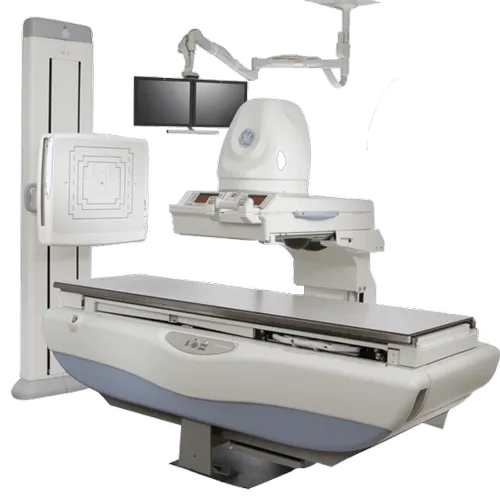

CT Scanners (Computed Tomography)
Purpose: Combine multiple X-ray images to create detailed cross-sectional views of the body.
• Use Cases: Used for diagnosing tumors, internal injuries, and diseases such as cancer.
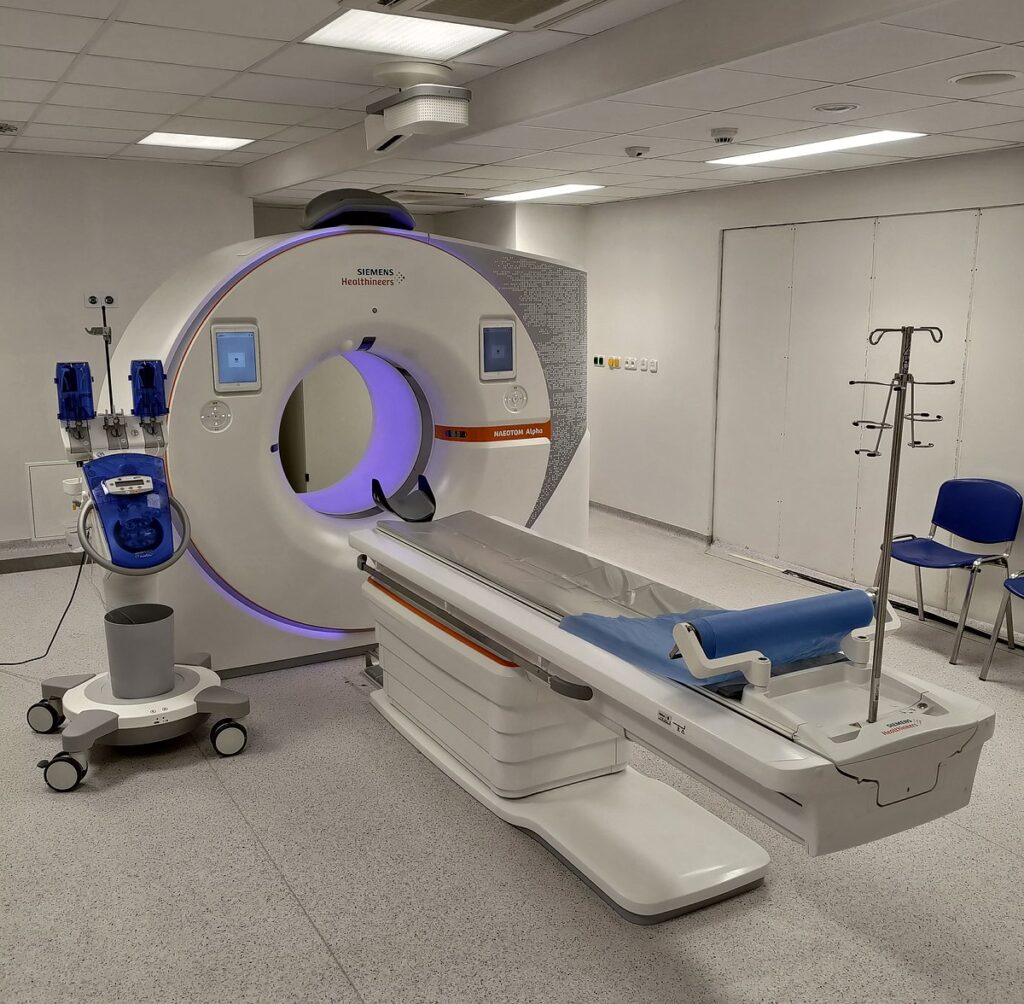
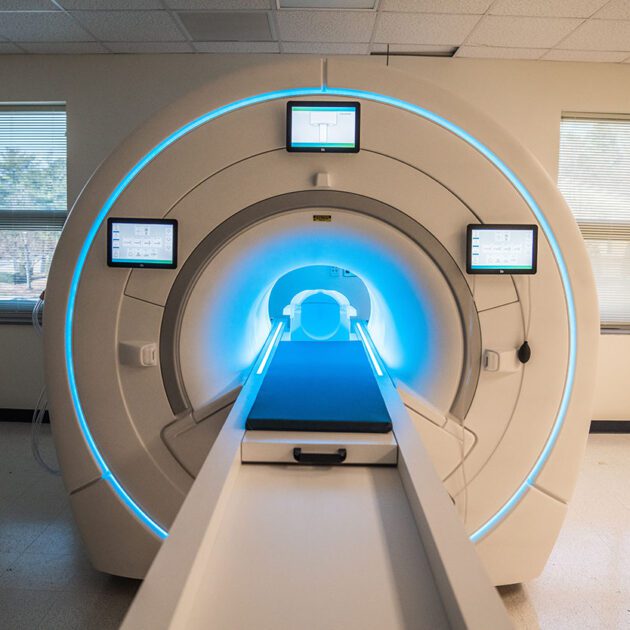
MRI Machines (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Purpose: Use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues, bones, and organs.
• Use Cases: Common in neurology (brain imaging), orthopedics, and oncology.
• Features: Non-invasive, radiation-free, with superior soft tissue contrast.
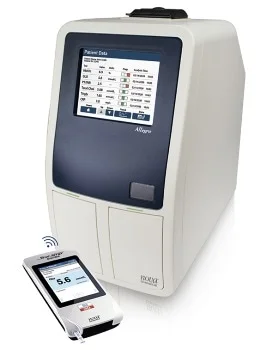
Blood Analyzers
Purpose: Analyze blood samples to measure components such as red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets.
• Use Cases: Used in labs and hospitals for routine blood tests and diagnosing infections, anemia, or other conditions.
• Examples: Hematology analyzers, chemistry analyzers.
Endoscopes
Purpose: Allow visual inspection of internal organs (like the gastrointestinal tract) using a camera inserted through natural openings or small incisions.
• Use Cases: Diagnose issues such as ulcers, tumors, or blockages.
• Types: Flexible or rigid endoscopes, depending on the procedure.

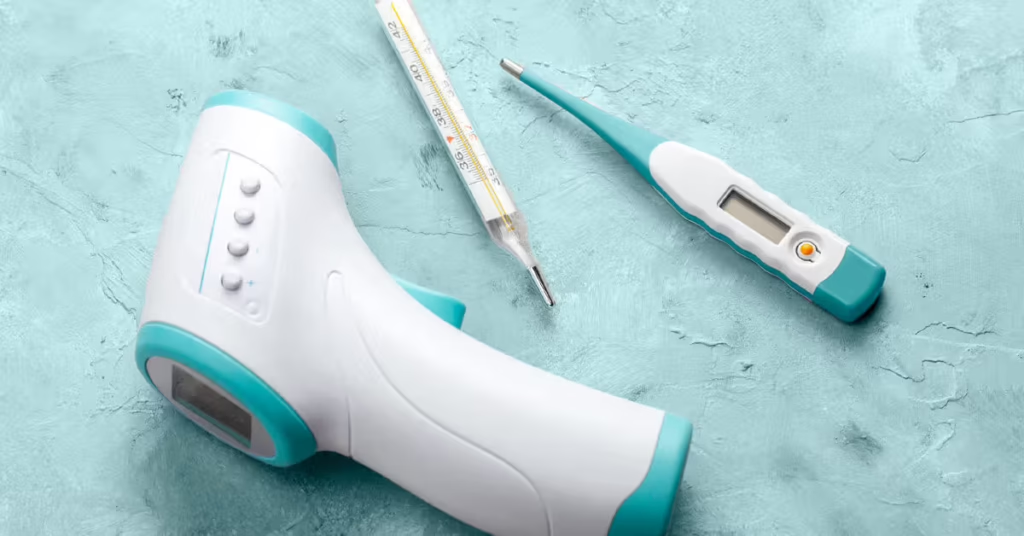
Thermometers
Purpose: Measure body temperature to detect fever or infections.
• Use Cases: Commonly used in all medical settings.
• Types: Digital thermometers, infrared (non-contact) thermometers, and tympanic (ear) thermometers.
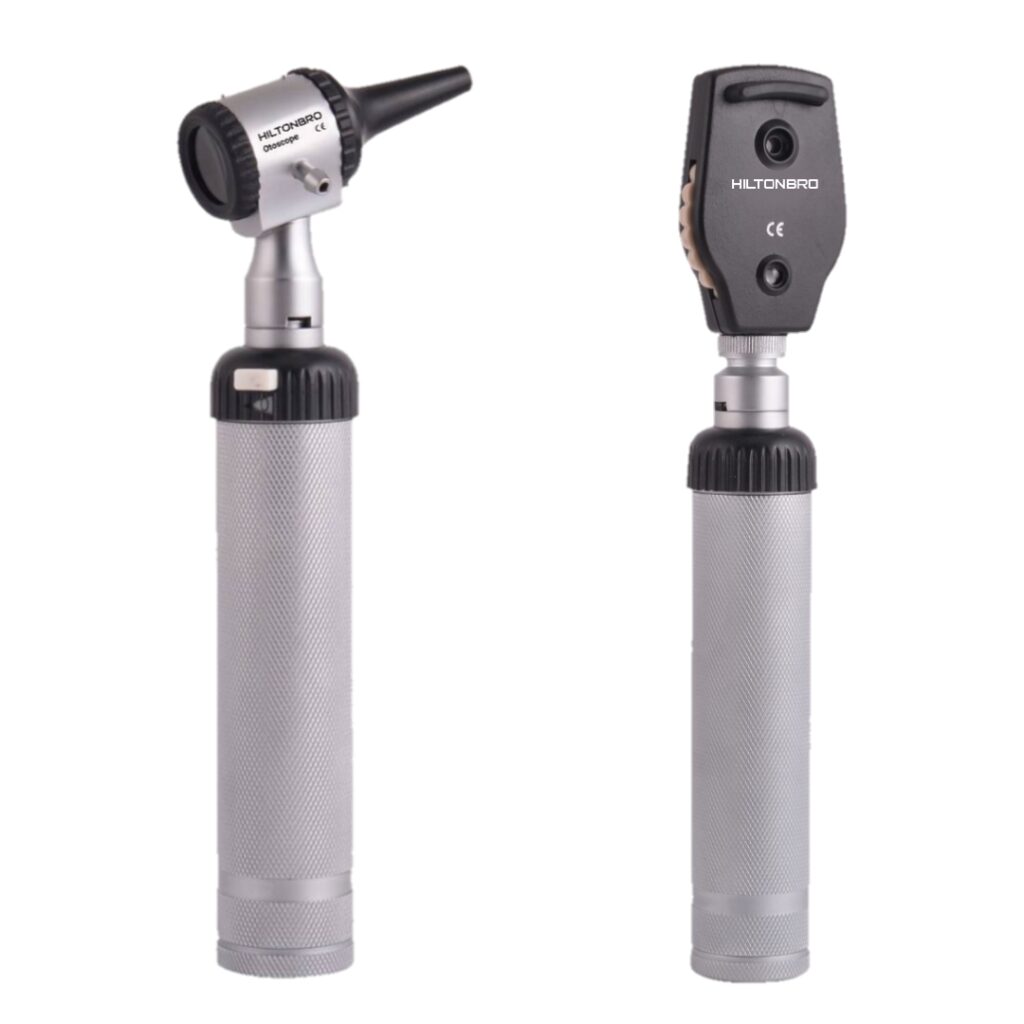
Ophthalmoscopes and Otoscopes
Ophthalmoscope Purpose: Examine the interior of the eye, including the retina.
• Otoscope Purpose: Inspect the ear canal and eardrum for infections or blockages.
• Use Cases: Used by general practitioners, ophthalmologists, and ENT specialists.

Spirometers
Purpose: Measure lung function by assessing airflow in and out of the lungs.
• Use Cases: Diagnose and monitor respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD.
• Features: Portable and computerized versions for detailed analysis.
Doppler Machines
Purpose: Measure blood flow and detect blockages in blood vessels.
• Use Cases: Commonly used in cardiology, vascular medicine, and obstetrics to check fetal blood flow.

Hospital Equipment
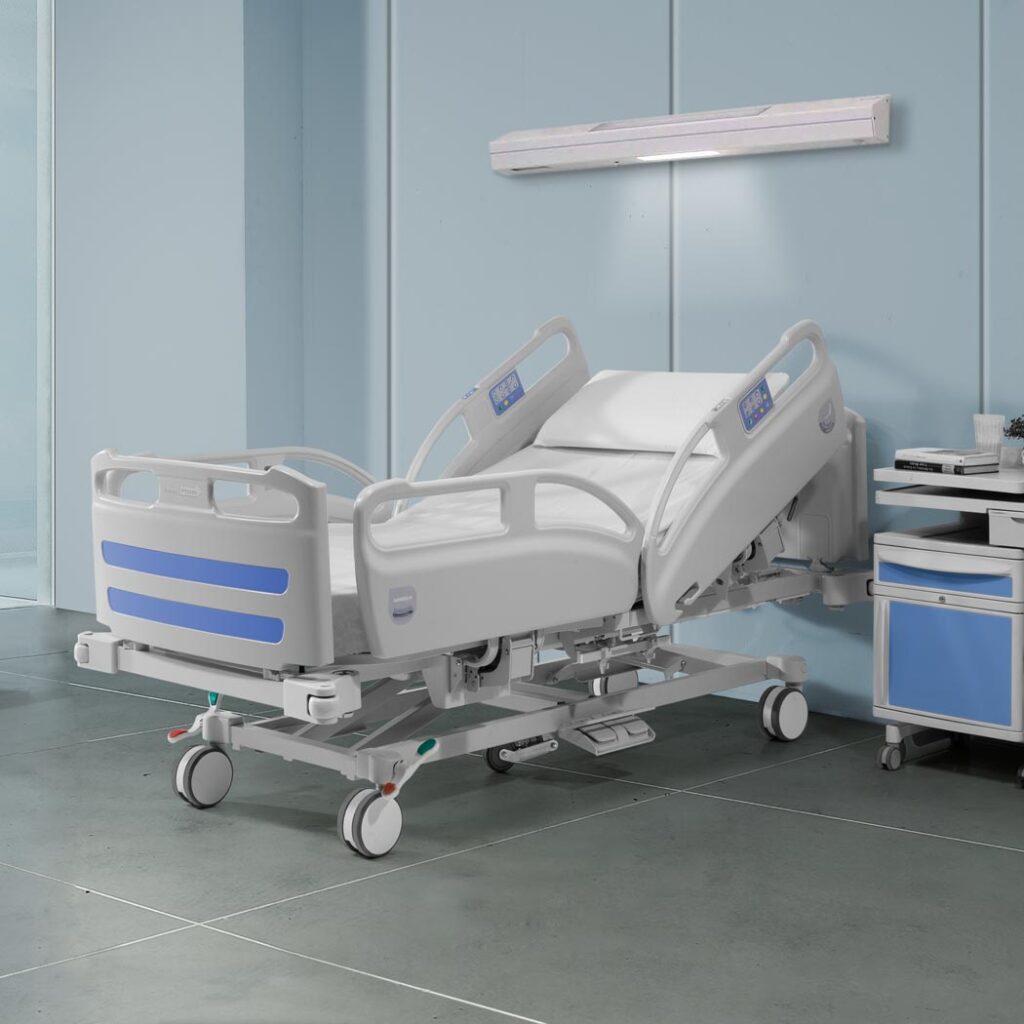
Hospital Beds
Purpose: Adjustable beds that provide comfort and support for patients during their stay.
• Features:
• Electrically or manually adjustable head, foot, and height positions.
• Side rails for safety.
• Options like ICU beds with integrated monitoring systems.
• Use Cases: Suitable for general wards, ICUs, and recovery rooms.
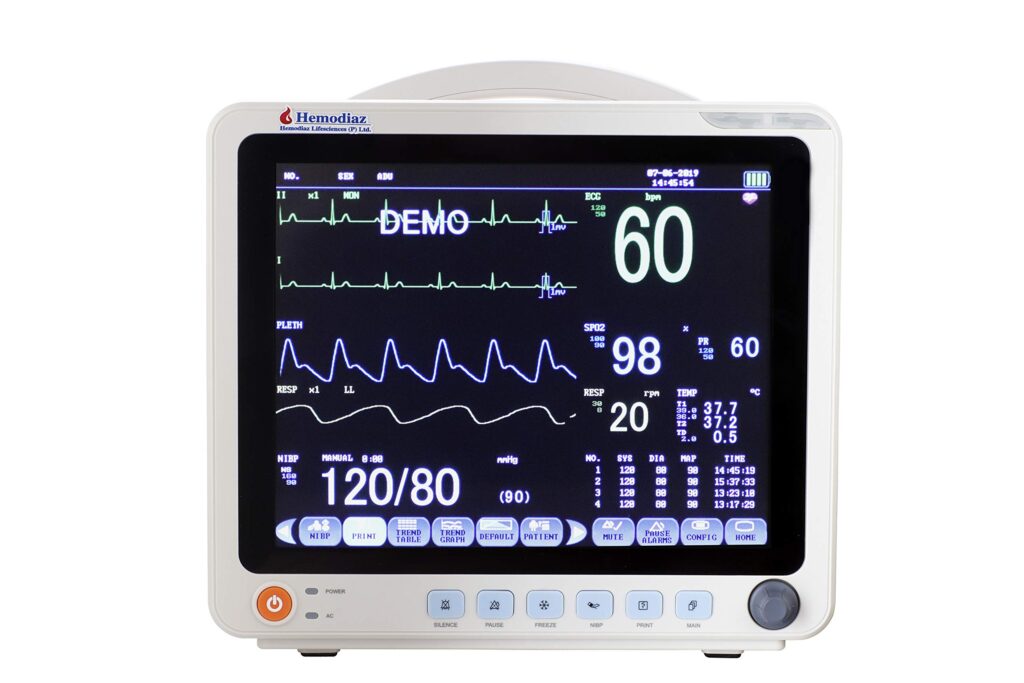
Patient Monitors
Purpose: Continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate.
• Features:
• Alarm systems for abnormal readings.
• Multi-parameter displays for real-time data.
• Use Cases: Used in intensive care units (ICUs), operating rooms, and
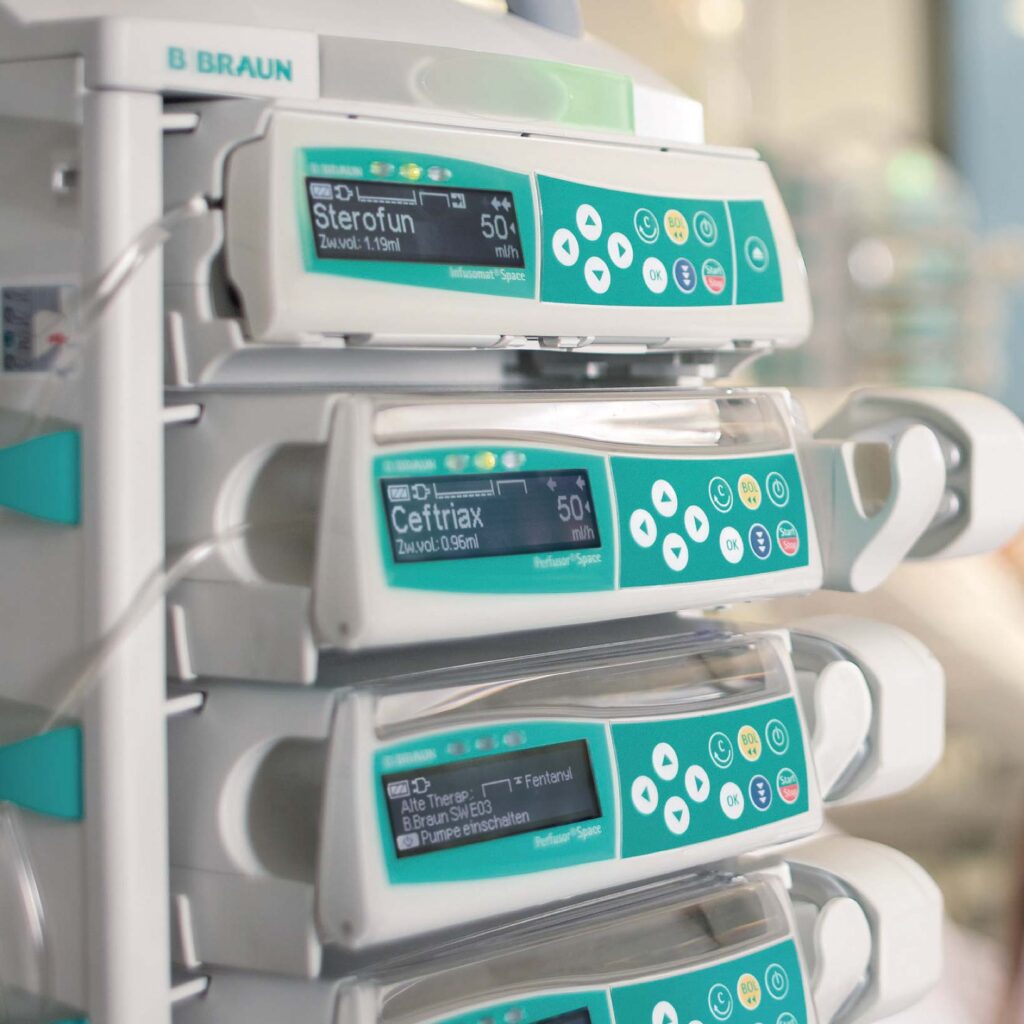
Infusion Pumps
Purpose: Deliver precise amounts of fluids, medications, or nutrients into a patient’s bloodstream.
• Features:
• Programmable settings for flow rate and dosage.
• Compatibility with various types of medications.
• Use Cases: Used for chemotherapy, IV fluids, or pain management.
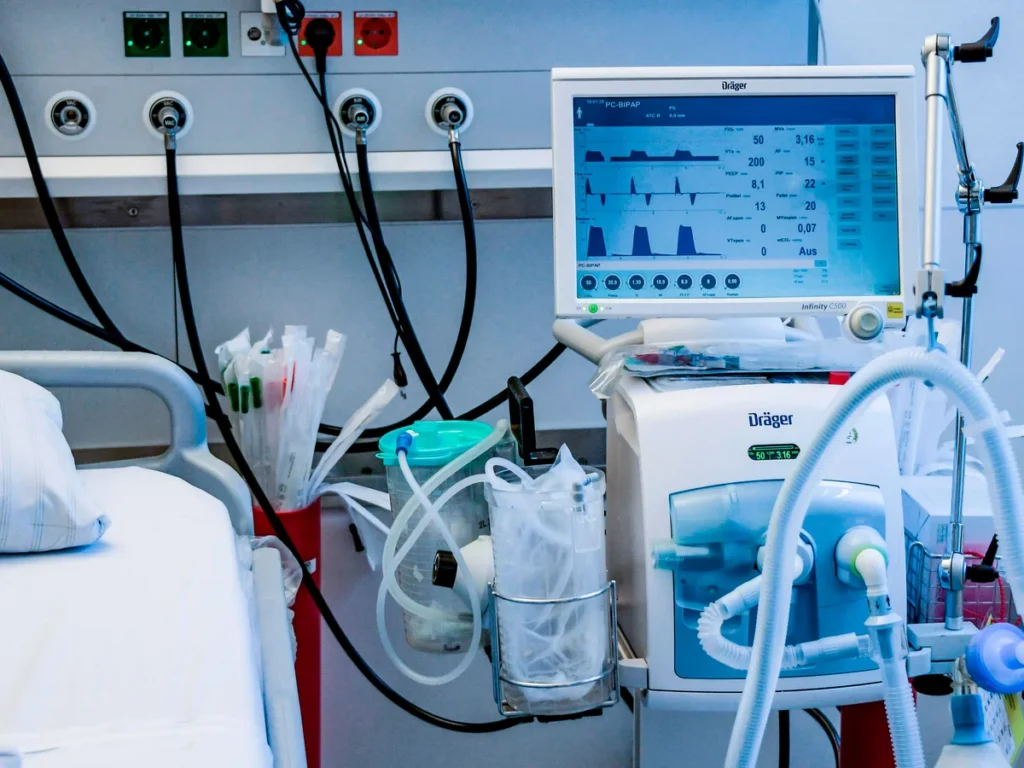
Ventilators
Purpose: Assist patients who are unable to breathe adequately on their own.
• Features:
• Modes for invasive and non-invasive ventilation.
• Adjustable oxygen levels and pressure settings.
• Use Cases: Critical for ICU patients, especially those with respiratory failure or undergoing surgery.
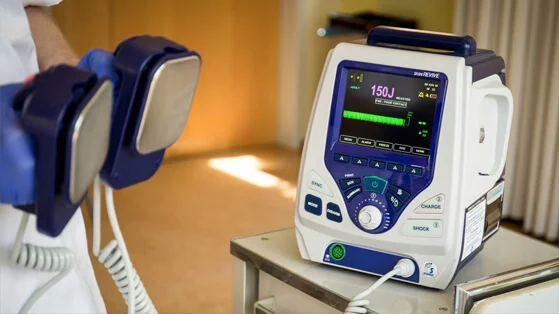
Defibrillators
Purpose: Restore normal heart rhythm in patients experiencing cardiac arrest.
• Features:
• Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) for emergency use.
• Advanced defibrillators for clinical settings.
• Use Cases: Used in emergency rooms, ambulances, and hospital wards.
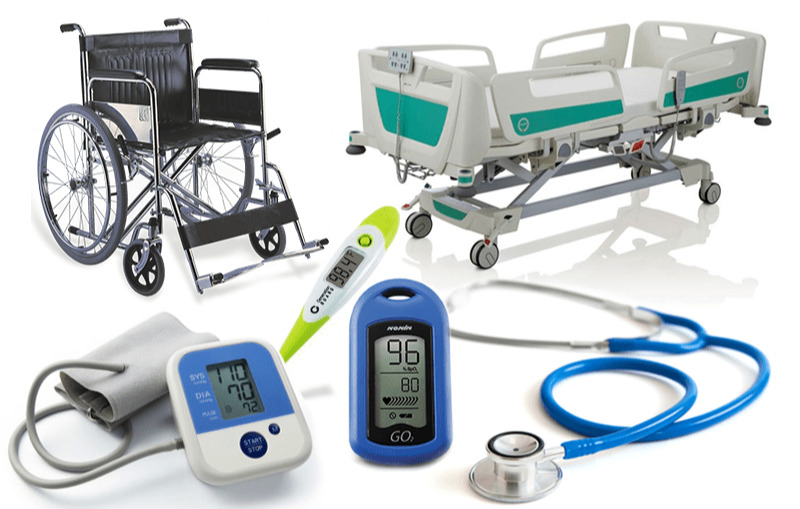
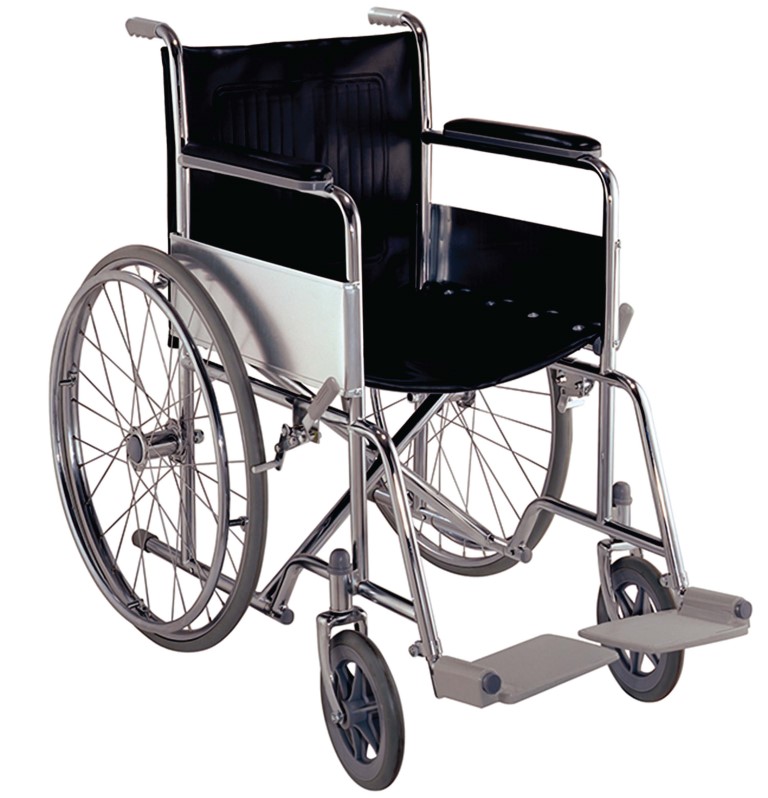
Wheelchairs and Stretchers
Purpose: Transport patients safely within the hospital.
• Features:
• Foldable wheelchairs for mobility.
• Adjustable stretchers with shock-absorption systems.
• Use Cases: Emergency patient transport and daily movement within facilities.

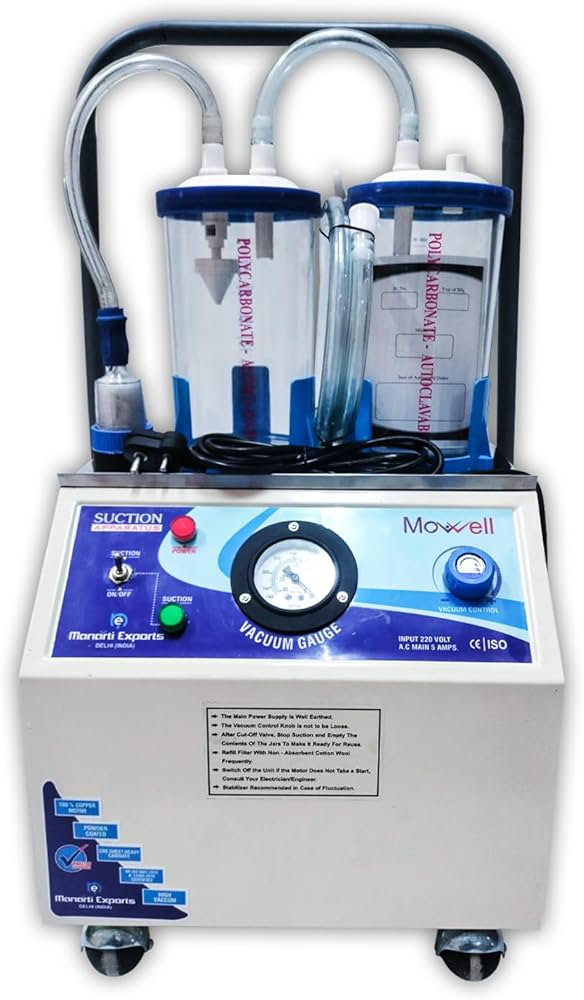
Suction Machines
Purpose: Remove secretions, blood, or other fluids from a patient’s airway or surgical site.
• Features: Portable and wall-mounted units.
• Use Cases: Common in surgical suites, ICUs, and emergency care.
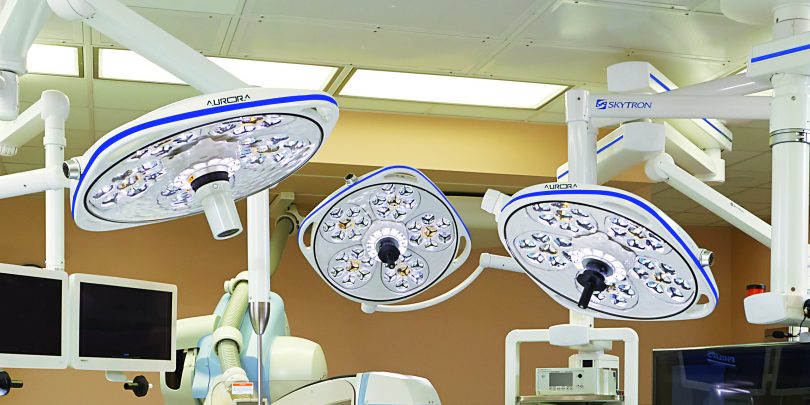
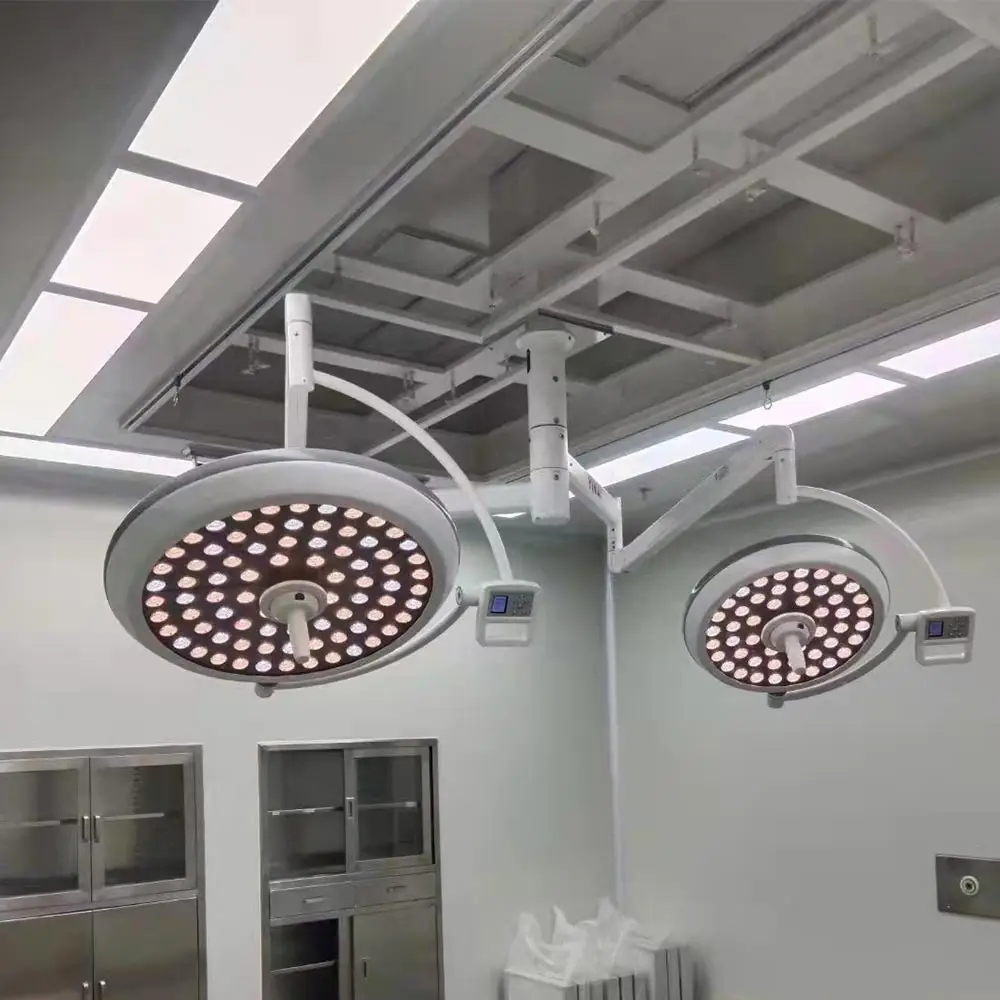
Surgical Lights
Purpose: Provide bright, shadow-free lighting during surgical procedures.
• Features:
• Adjustable brightness and focus.
• LED options for energy efficiency.
• Use Cases: Essential for operating rooms and minor procedure areas.
Oxygen Concentrators and Cylinders
Purpose: Deliver a continuous supply of medical-grade oxygen to patients with respiratory issues.
• Features:
• Portable models for mobility.
• High-capacity units for ICUs.
• Use Cases: Used in general wards, ICUs, and home care settings.

Dental chairs are the cornerstone of any dental clinic. There are various types, including:
Fully Automatic Dental Chairs: These chairs come with advanced automatic settings for patient comfort and ease of use for the dentist.
Ergonomic Design Chairs: Designed to reduce fatigue for both the patient and the dentist, providing maximum support.
LED Dental Chairs: Equipped with integrated LED lights for optimal lighting during treatments.

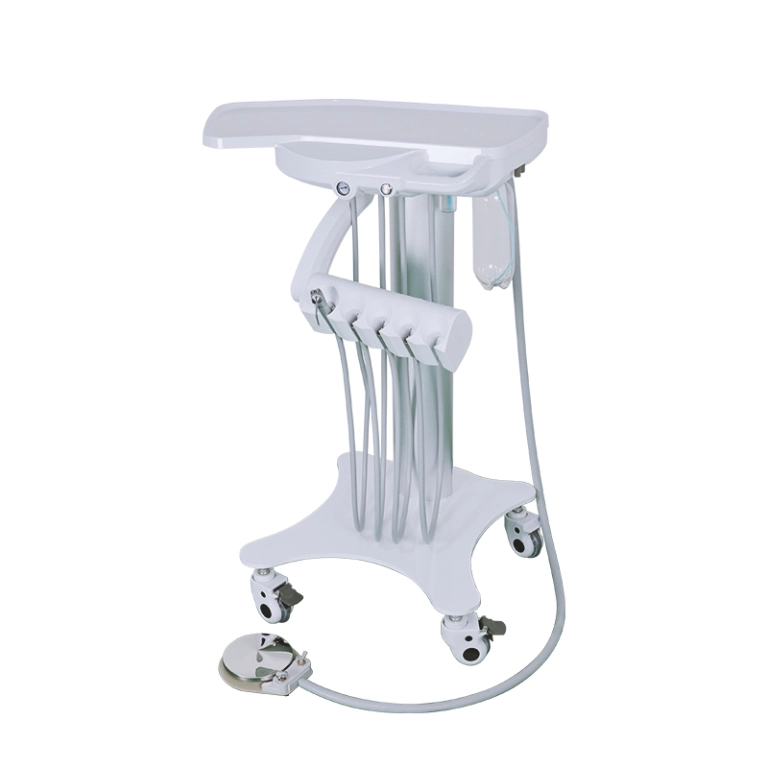
Portable Dental Chairs: Lightweight and portable chairs ideal for mobile clinics or temporary setups.
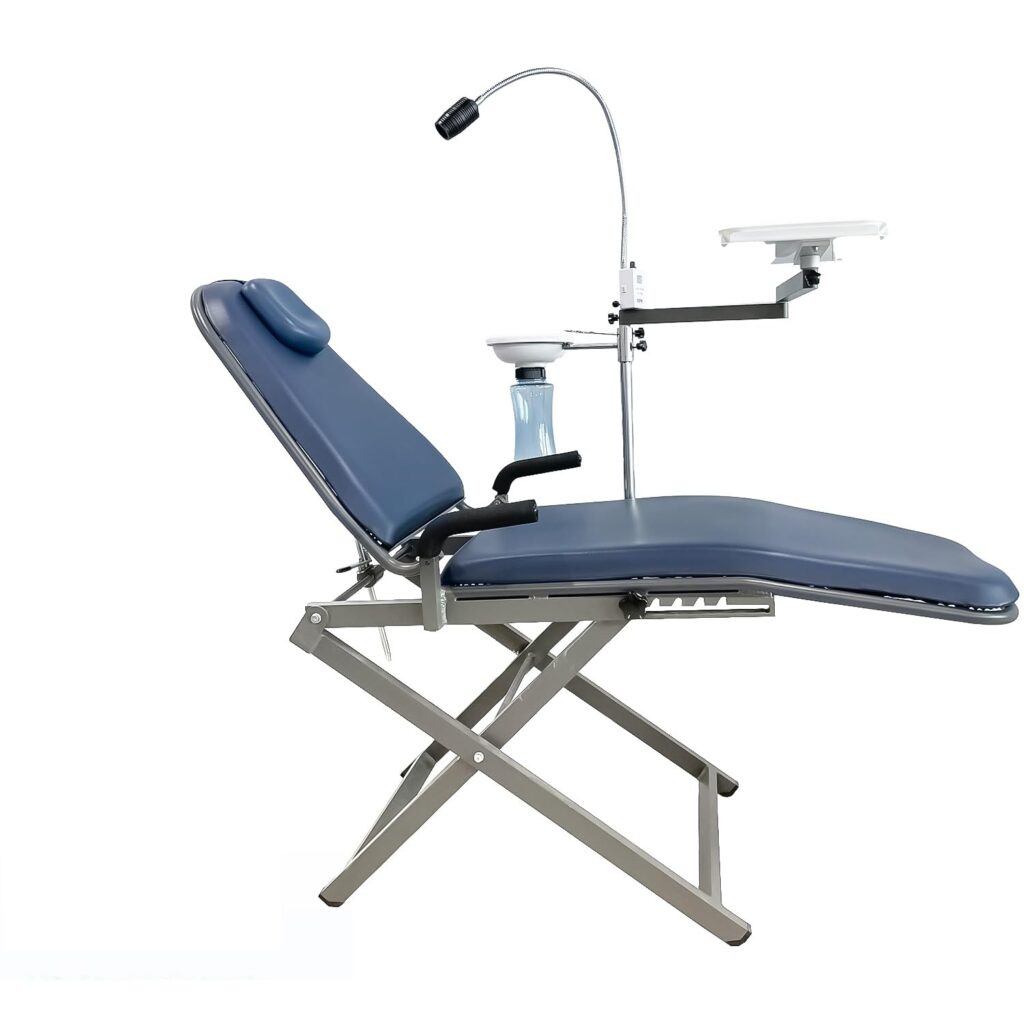
Dental Units
Dental units are comprehensive systems that include essential tools for dental procedures:
ntegrated Dental Units: Fully equipped units with built-in lights, handpieces, and pedals.

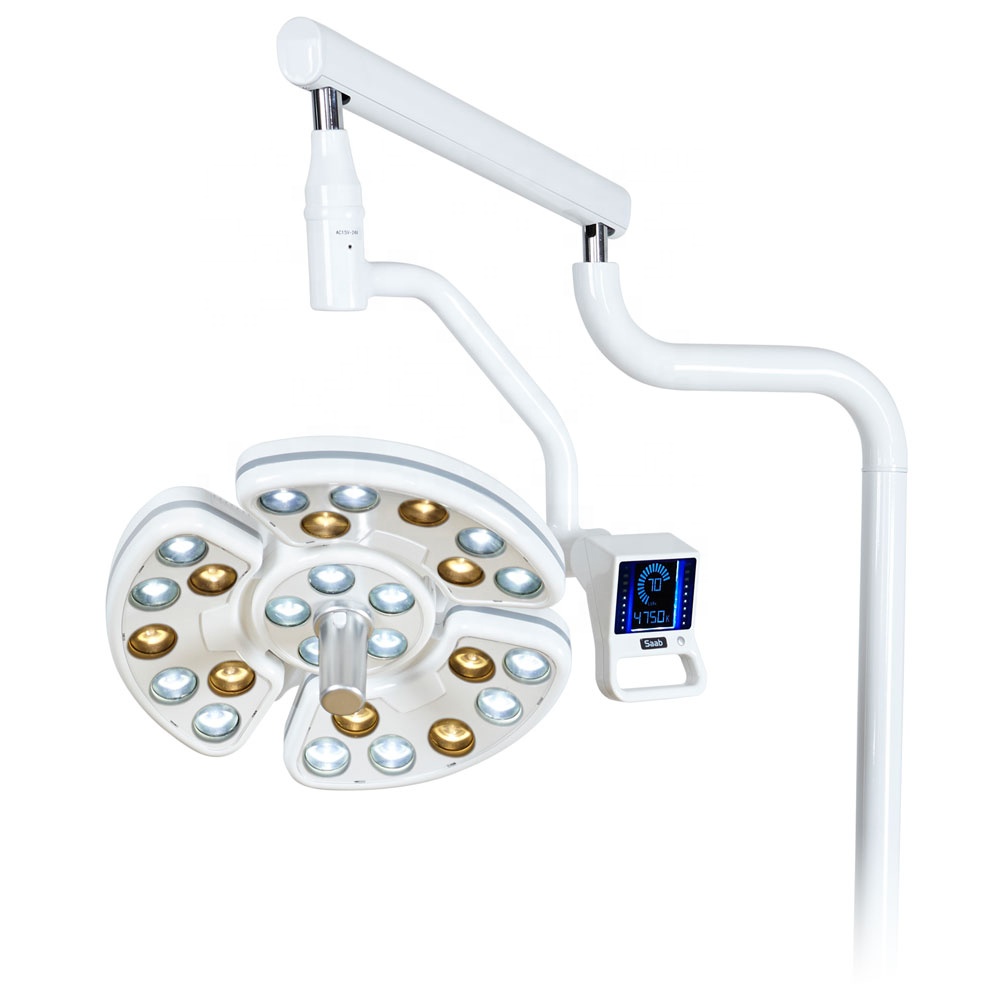
Dental Lights
Dental lights ensure proper visibility during procedures:
• LED Dental Lights: Energy-efficient lights with cool brightness for precise treatments.

Adjustable Intensity Lights: Lights with customizable intensity to meet specific procedural needs.
Ceiling-Mounted or Unit-Mounted Lights: Lights mounted on dental units or suspended from the ceiling for flexible positioning.
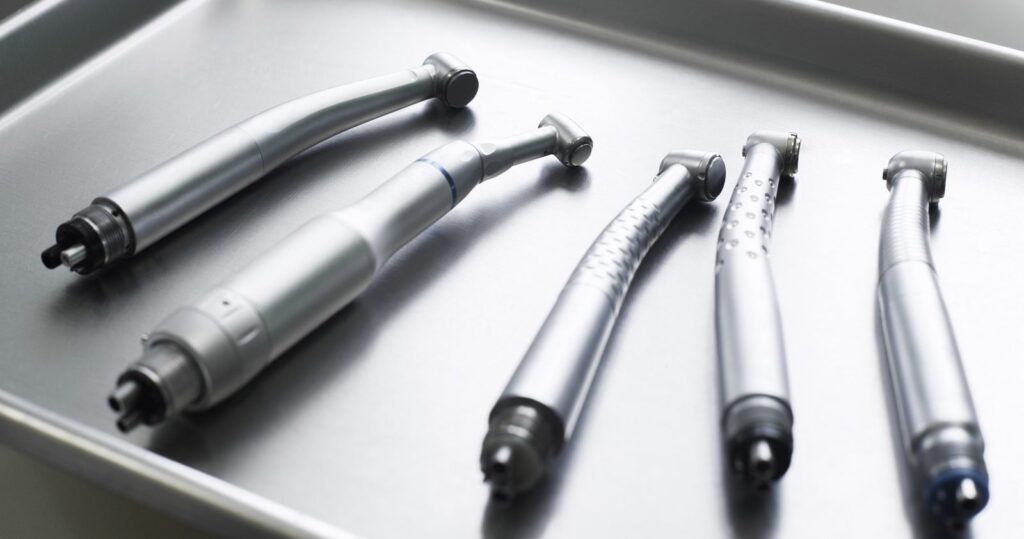
Dental Tools & Handpieces
Essential tools used in various dental treatments include:
• High-Speed Handpieces: Used for cutting and shaping teeth with high precision and speed.
• Low-Speed Handpieces: Ideal for polishing, cleaning, and sensitive procedures.
• Ultrasonic Scalers: Instruments that use ultrasonic vibrations to remove tartar and plaque.
• Dental Turbines: High-precision tools for fast and accurate dental work.

Sterilization Equipment
Hygiene and sterilization are critical in dental practices:
• Autoclaves: Steam sterilizers that use heat and pressure to sterilize dental tools.
• UV Sterilizers: Devices that use ultraviolet light to disinfect small tools.
• Ultrasonic Cleaners: Machines that use ultrasonic waves to clean debris and contaminants from tools.
